Radiological Approach to Infectious Diseases of the Spine
1. Terminology
- Discitis: Infection limited to the intervertebral disc
- Spondylitis: Infection of the vertebral body
- Spondylodiscitis: Involvement of both the intervertebral disc and adjacent vertebral bodies
2. Etiology and Pathogenesis
- Hematogenous spread – the most common route (especially Staphylococcus aureus)
- Direct inoculation – post-surgical infections
- Contiguous spread – from psoas abscess, retroperitoneal infections, etc.
3. Imaging Modalities
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Gold standard for diagnosis
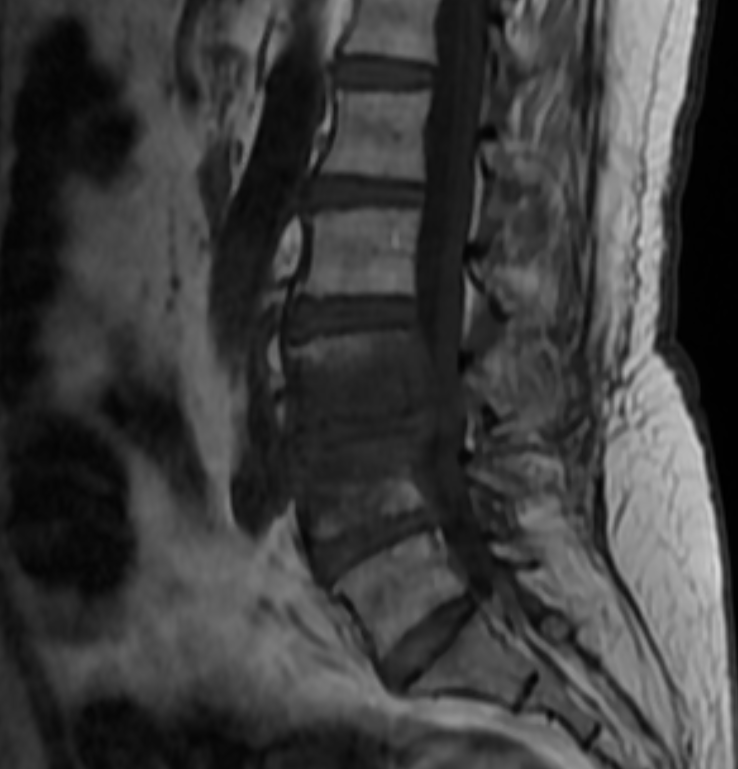
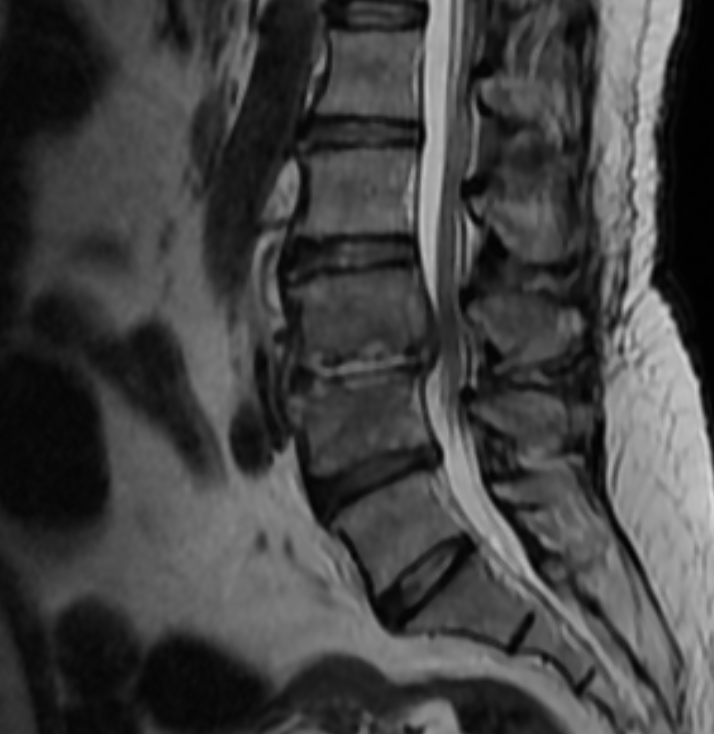
- Early findings: Low signal on T1-weighted images, high signal on T2/STIR
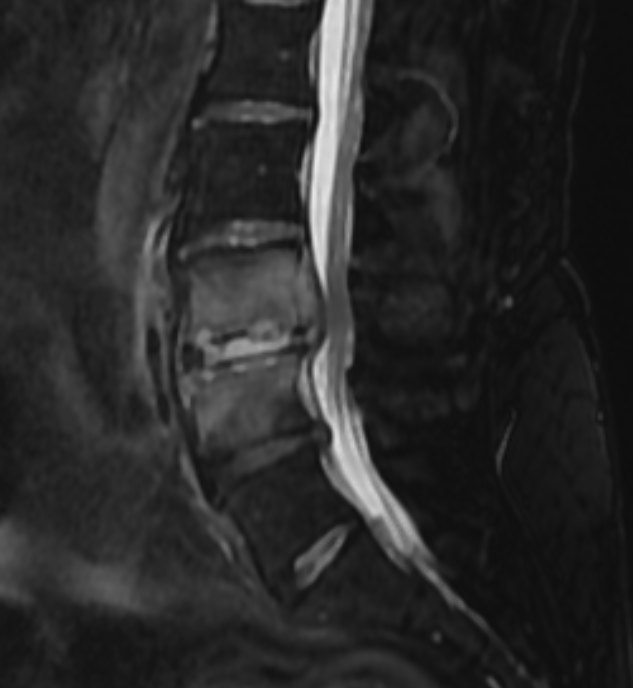
- Contrast-enhanced MRI: Demonstrates epidural/paraspinal abscesses and granulation tissue
- Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI): Differentiates abscess from necrotic tissue
Computed Tomography (CT)
- Useful for visualizing bone erosion, destruction, and sequestrum
- Guides biopsy/aspiration procedures
Plain Radiography
- Usually normal in early stages
- Late findings include disc space narrowing, vertebral endplate erosion
4. Differential Diagnosis
- Modic changes (especially Type 1)
- Metastatic lesions
- Traumatic vertebral fractures
- Osteoporotic changes
5. Summary of Radiological Findings
| Modality | Typical Findings |
|---|---|
| MRI T1 | Loss of vertebral and disc signal |
| MRI T2/STIR | High signal, marrow/soft tissue edema |
| Contrast MRI | Enhancement of the disc and adjacent vertebra; possible epidural collection |
| CT | Endplate erosion, bone destruction |
6. Clinical Pearls
- Disc involvement on MRI strongly suggests infection (rare in tumors)
- Epidural abscess requires urgent surgical consultation
- In early stages, MRI findings may be subtle; repeat imaging if clinical suspicion remains high
Conclusion
MRI is the primary modality for evaluating infectious diseases of the spine. Early and accurate diagnosis facilitates prompt initiation of antimicrobial and/or surgical treatment, reducing morbidity and mortality.
A 62-year-old female patient with a history of diabetes presented with low back pain. MRI was performed.